Google Cloud Products offer a variety of solutions to businesses that want to transform digitally. In this post we will take a look at some of the Google Cloud Products and Services, and then discuss how to approach a business transformation with the help of Google Cloud.
The post contains reference to the Google Cloud website and training videos on Coursera
What is Cloud?
Cloud computing refers the technology and processes needed to store, manage, access, and process data over the internet rather than on local machines or local servers.
- On demand IT Services – network, computers, software, security systems- all combined.
- Reduces the need for an organization to make upfront investments in hardware, hence lowering capital expenditure.
- Cloud enables rapid scaling i.e. no need to wait to buy additional hardware for handling increased data storage requirements or increased computing power.
- Cloud provides quick and easy access to a wide range of new technology solutions such as machine learning and artificial intelligence, enabling organizations to innovate faster and stay agile.
Who Are The Major Cloud Players?
The most popular providers of Cloud Products and Services are the following:
- Google Cloud
- Amazon Web Services
- Microsoft Azure
- IBM Cloud
As organizations across the world realize the benefits of cloud computing over the traditional IT infrastructure, they aim for digital transformation. Organizations want to stay competitive and jump off the burning platform on to the next generation technology. Cloud Computing has seen rapid growth in the past few years and will continue to do so in the foreseeable future.
What is a Burning Platform?
A Burning Platform is an existing technology or process that is at risk of becoming irrelevant in the near future. Some companies take a leap of faith and try the next technological invention, while some do not. A lot of companies fail to jump off the burning platform and lose out to the competition that adopts the new technology.
Successful Company: Nintendo – started with Japanese playing cards, then leveraged technology of each era to keep leaping from console to mobile gaming to cloud console ‘Switch’. They focused on ‘why’ and using technology to their advantage rather than perceiving it as a threat.
Unsuccessful Company: Encyclopedia companies – they were more focused on the books rather than transferring knowledge via the technology of the era.
What are the Benefits and Superpowers of the Cloud?
Collaboration
Undoubtedly, collaboration is a superpower of the cloud. Seamless video meetings, simultaneous document editing, prompt reviews – everything increases the organizational productivity manifold.
Perception
Cloud enables the mapping and understanding of patterns in huge amounts of data and helps you perceive trends, correlations or anomalies easily.
Categorization
When there is a lot of data, more than what humans can manually process, cloud superpowers can help. Categorized huge amounts of data in two or more categories through machine learning is another superpower of the cloud.
Recommendation
Taking a look at your histrionical data or behavior, a recommendation can be made to you. Cloud helps organizations, by processing huge amounts of data, in picking and recommending relevant products and services to customers.
Prediction
Forecasting accurately can help organizations plan better. Be it weather forecast for a business that rents out boats, or inventory forecast for an e-commerce giant, the predictive capabilities of cloud can bring great value to business.
What Are The Four Types of Cloud Services?
- IaaS – Infrastructure as a Service
- SaaS – Software as a Service
- PaaS – Platform as a Service
- Serverless Computing
What is IaaS?
IaaS or Infrastructure as a Service allows an organization to move some or all IT infrastructure to cloud. By choosing IaaS, the company reduces the setup time and costs, and chooses to shift its IT Spending to MORE operating expenses and LESS capital expenses.
What is SaaS?
SaaS or Software as a Service allows organizations to use cloud-based apps over the Internet. A common example of SaaS is a cloud based document editing tool.
What is PaaS?
PaaS or Platform as a Service is an environment where you can purchase resources to develop and deploy solutions such as basic apps or more sophisticated applications.
What is Serverless Computing?
With Serverless Computing, developers can focus more on building business applications rather than focusing on managing the IT infrastructure. Serverless is named so because the developer doesn’t have to worry about managing the infrastructure. The cloud service provider manages it to increase the developer productivity.
Types of IT Infrastructure
On Premises
As the name suggests, the organizations own everything on their premises. They own the data centers, servers, security measures, and real estate to store all of this. On an ongoing basis they also have to pay for the maintenance of this infrastructure as well.
Collocation
In Collocation, multiple organizations share the data center, the cost of hosting the infrastructure is reduced this way. However, maintenance costs are still to be paid by the organizations.
Virtual Machine
A virtual machine is a software image that works like an actual computer. Virtual Machines share a pool of hardware and processing power, making the operations efficient and lowering operating costs. They can be on-premises or collocated. The limitation of virtual machines, however, is that the physical capacity of the hardware is still capped.
Outsourced Infrastructure
To break free from the limitations of on-premise, collocation and virtual machines, organizations can choose to outsource some or all of their IT infrastructure to a cloud service provider sucha as Google Cloud, Microsoft Azure, or Amazon Web Services. Many organizations are increasingly doing so!
Single (Private), Hybrid, and Multi-Cloud Architectures
When transforming their IT Infrastructure, organizations can choose to go for a private, hybrid or multi-cloud architecture.
Private Cloud
Private cloud is where an organization has virtualized service in its own data centers to create its own private on-premises environment. This might be done when an organization has already made significant investments in its own infrastructure or if, for regulatory reasons, data needs to be kept on-premises.
Hybrid Cloud
Hybrid cloud is where an organization is using some combination of on-premises or private cloud infrastructure and public cloud services. This is the situation many organizations are currently in. Some of their data and applications have been migrated to the cloud. Others remain on-premises, and interconnect between the private and public clouds allow interoperability.
Multi Cloud
Multi-cloud is where an organization is using multiple public cloud providers as part of its architecture. In this case, the organization needs flexibility and secure connectivity between the different networks involved. An organization might choose to use the hybrid cloud or multi-cloud if they want to incorporate specific elements of a public cloud in order to take advantage of the key strengths of that provider. For example, many organizations see enormous benefits from using Google’s BigQuery data analytics tool, a serverless application that scales to multi-petabyte datasets, but may keep the core applications generating the data to be processed on-premises.
Moving to Google Cloud
When organizations decide to move to a hybrid or multi-cloud infrastructure, they want the process to be secure and painless. Google Cloud is open cloud that gives the users control over their data move and IT deployments. With the use of open APIs, Google services are compatible with other open source products and services.
Open Cloud
TensorFlow, for example, is an open source library developed at Google. Machine Learning scientists can freely leverage TensorFlow for their projects.
Kubernetes is a system for automating application deployment, scaling, and management using a concept known as containerization.
Anthos is an application modernization platform. It enables modernization of existing applications. Anthos allows you to build an application and run it wherever you want, on premises, on Google Cloud, or in a different public cloud such as AWS or Azure.
By having the concept of open cloud, Google helps speed up the process of application development.
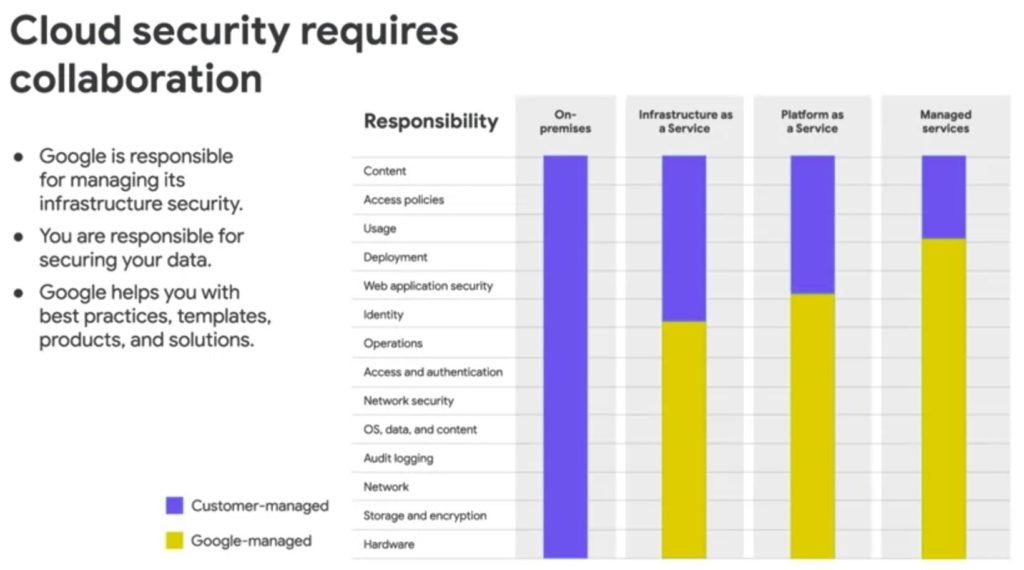
How is the Security on Google Cloud?
Google Cloud has a multilayer approach to Security. The following are Six Security Layers:
1. Hardware
First layer of security is the hardware layer. Custom built hardware and embedded Titan Chip ensure integrity by performing checks every time the machine boots up.
2. Software
Titan micro controller verifies the operating systems and deployed software stack. The server is not allowed onto the network until a server’s good health is confirmed.
3. Storage
At Google Cloud, all data at rest is also encrypted by default, to help guard against unauthorized access. First, the data is broken down into many pieces in memory.
- These pieces of data are encrypted with their own data encryption key or DEK.
- DEKs are then encrypted a second time with a wrap key, generating a key encryption key or KEK.
Encrypted chunks and wrapped encryption keys are distributed across Google’s infrastructure.
If an encryption key is compromised, hacker can only access one tiny piece of data which, just by itself, would be unreadable.
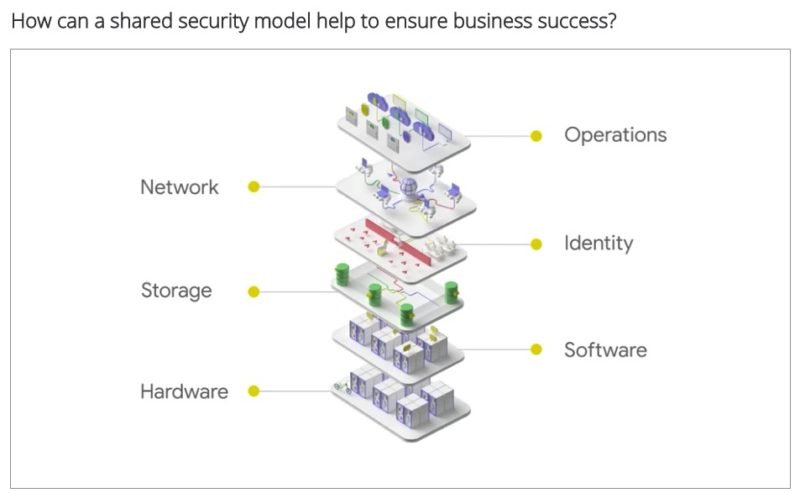
4. Identity
Google Cloud operates on a zero trust model i.e. every machine or user needs to authenticate at every step if they want to access any data or service.
5. Network
Encryption in transit protects data as it moves across a network. The data in transit, that is all the data, moving into and out of Google’s Cloud infrastructure is encrypted in transit.
6. Operations layer
At Google, a global team of 900+ security experts, monitor the system for attacks and other issues, 24 hours a day, 365 days a year. Their role is to detect attacks and other issues, and promptly respond to them.
In addition to these multiple layers of security, Google Cloud has an array of features and policies that its customers can use to control access to their data.
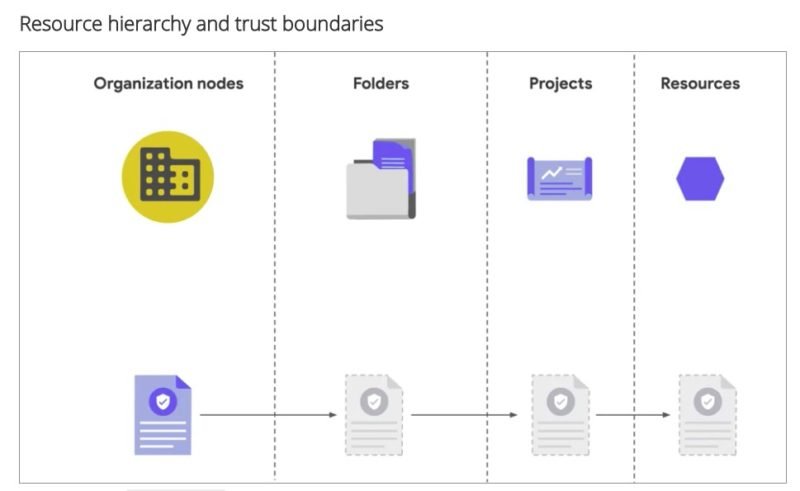
Google Cloud Security: Hierarchy and Trust Boundaries
This is the hierarchy: Nodes > Folders > Projects > Resources.
- Resources – Products and services such as a storage bucket or a compute engine
- Project – Resources can be assigned to projects. Each resource belongs to exactly one project.
- Folder – A Folder can contain projects or other folders.
- Organization Node – Contains folders
Google Cloud IAM
Cloud IAM helps control access and maintain security of data – who can do what on which resource
Identity and Access Management (IAM) only allows access, it does not deny access. What that means is that the more generous policy takes effect if higher level (Folder level) policy grants less access (say, View only) and lower level (Project level) policy grants more access (say, View and Edit), the user will be granted View and Edit access on the Project.
IAM is about managing Who can do What on Which Resource.
- Who (can be a google account, or a user group or a service account)
- Can Do What (defined by an IAM role – there are three types of IAM roles in Google Cloud)
- Primitive Roles: Viewer, Editor, Owner (Owner can also set up Billing)
- Predefined Roles: Typical job roles of people, such as sales executive, finance manager etc.
- Custom Roles: Allows setting up more granular control
- On Which Resource (Google Cloud Products and Services)
Google Cloud Featured Products
Google Cloud offers an array of products and solutions for organizations big and small. Some of the popular products are the following.
- BigQuery
- Cloud Storage
- Anthos
- Cloud Functions
- DataFlow
- Compute Engine
- Cloud SQL
- Google Kubernetes Engine
- Cloud Run

Google Cloud has a lot more products on offer, let’s take a look at some more of them by category.
Google Cloud Core Products and Solutions
Let’s take a look at Google Cloud products in 4 Core Categories
Compute
- Compute Engine: Virtual Machines that run in Google’s data centers.
- Google Kubernetes Engine: Environment for running containerized apps.
- App Engine: Serverless application platform for apps and back ends.
- Cloud Functions: Function as a Service (FaaS) to run code without managing servers.
Storage
- Cloud Storage: Object storage for unstructured data.
- Cloud SQL: Database for SQL Server, MySQL, and PostgreSQL.
- Bigtable: Cloud native database for large workloads.
- Cloud Spanner: Cloud native relational database.
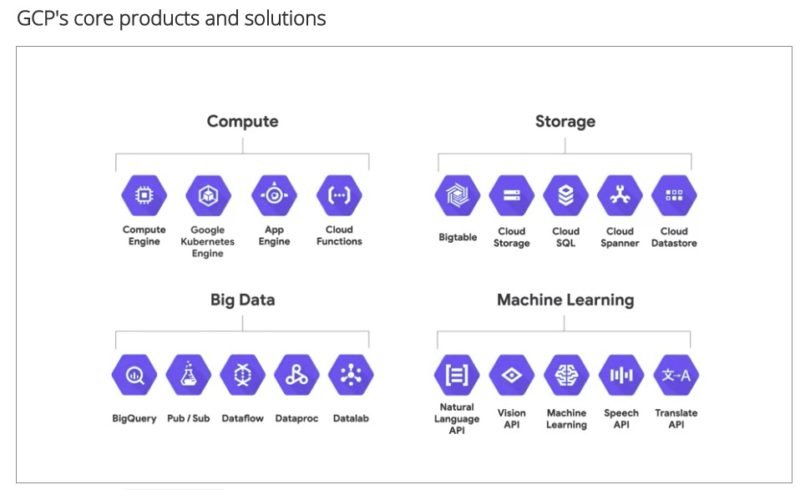
Big Data
- BigQuery: Data warehouse for business agility and insights.
- Pub/Sub: Messaging service for event ingestion and delivery.
- Dataflow: Stream analytics.
- Dataproc: Service for running Apache Spark and Apache Hadoop clusters.
Machine Learning
- Cloud Natural Language: For classification of unstructured text and sentiment analysis.
- Vision AI: Custom build a training model or use pre-trained models to detect emotion, understand text etc.
- AutoML: Custom ML model training and development.
- Text to Speech: Convert text to speech in 40+ languages
- Speech to Text: Recognize and transcribe speech in 125+ languages
We will get into details of some of these products and services.
Google Cloud Products for Compute
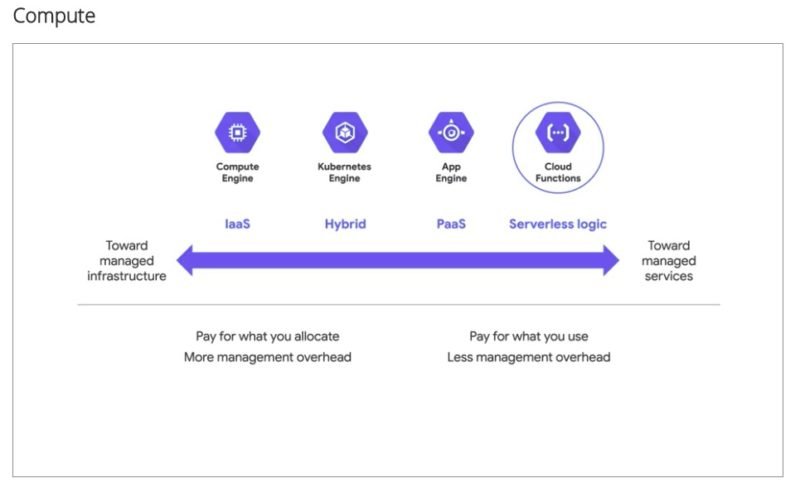
- Compute Engine (IAAS): request Virtual Machines. Unlimited processing power – configure as desired. Rapid Autoscaling for traffic spikes. Per second billing. Use cases – DNA sequencing, media rendering. clients – Spotify (music streaming)
- Kubernetes Engine (HYBRID): containerization. client – Signify (smart lighting)
- App Engine (PAAS): eliminate need to buy, build and operate computing hardware and other infrastructure. client – IDEXX laboratories (veterinary care)
- Cloud Functions (Serverless Logic): it provides a connective layer of logic that lets you write code to connect and extend cloud services. It’s an ideal solution to automate things without managing a server or runtime environment

Compute
- Cloud GPUs
- Compute Engine
- SQL Server on Google Cloud
- Cloud Run
- VMware Engine
- App Engine
Source: Google Cloud
Application Development
There are 5 standard patterns to switch to a cloud based application.
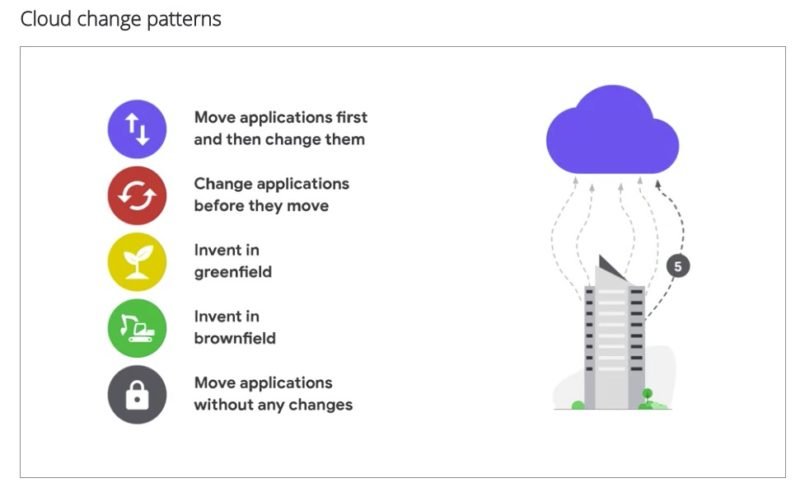
- Move applications first and then change them: relatively conservative approach. lift and shift for selected apps.
- Change applications before they move: more aggressive. rearchitect the apps first and then migrate to cloud.
- Invent in Greenfield: building entirely new infrastructure and applications. develop new products.
- Invent in Brownfield: invent new application in cloud that will replace an on-premise application. Switch happens after the new app is up and running.
- Move applications without any changes: modernizing infrastructure like moving data centers from on premise to cloud.
Challenges in Application Development
- Monolithic architecture: as it gets updated over time, the code base becomes bloated. It is difficult to change one part without breaking another. Implementing updates becomes lengthy.
- Microservice: Code base for each service is modular. Service can be updated and deployed independently. Each service can be scaled independently.
Adopting an automated continuous integration and continuous deployment approach, also known as CI/CD, can help you increase your application release velocity and reliability. With a robust CI/CD pipeline, you can test and roll out changes incrementally instead of making big releases with multiple changes. This approach enables you to lower the risk of regressions, debug issues quickly, and roll back to the last stable build if necessary.
GCP developer tools help you release software at a high velocity while balancing security and quality.
App Engine
Key features of the App Engine are the following:
- Allows you to build scalable web apps and mobile backends
- App engine manages hardware and networking infrastructure required to run code.
- Upload the code, google manages the app availability.
Google Cloud Products for Storage
Data can be broadly classified into two categories – Structured Data and Unstructured Data
- Examples of Structured Data: Customer records, names, dates of birth, addresses
- Examples of Unstructured Data: images, videos etc. can be stored as objects. Some unstructured data can be stored as BLOBs (binary large objects).
Google Cloud Products for Database (for Structured Data)

Database (Structured Data)
- Cloud Bigtable
- Cloud SQL
- Firebase Realtime Database
- Firestore
- Database Migration Service
- Cloud Spanner
Source: Google Cloud
Cloud SQL
It is a fully managed relational database management service, or RDBMS, that is compatible with common database management systems (MySQL, PostgreSQL, and SQL Server) and methodologies, and built on performance innovations in Compute Engine. It offers security, availability, and durability, and scalability. This makes it easy for organizations to set up, maintain, manage, and administer databases in the cloud.
Cloud Spanner
It is a fully managed database service, but it’s designed for massive, practically unlimited, global scale. It offers super high availability of 99.999%. Data is automatically and instantly copied across regions. This replication means that if one region goes offline, the organization’s data can still be served from another region. It also means that queries always return consistent and ordered answers regardless of the region. For example, if someone in the London office updates information in the database, that update is immediately available for someone in the New York office.
BiqQuery
BigQuery is a multi-cloud analytical database. That means it is both a storage service and powerful analysis service. It allows you to query very large databases quickly and analyze petabytes of data at fast speeds.
GCP Data Solutions: Cloud Storage for Unstructured Data
Cloud Storage provides different options based on required access so that an organization can tailor its object storage to its needs.

Storage (Unstructured Data)
- Cloud Storage
- Filestore
- Local SSD
- Cloud Storage for Firebase
- Google Workspace Essentials
- Cloud Data Transfer
Source: Google Cloud
Data that is accesses more often can be stored on MultiRegion or Regional Storage
MultiRegion Storage
Your organization might be storing data that is frequently accessed from around the world, for example, data that serves website content on mobile applications or streaming videos. For this type of data, Cloud Storage offers multi-regional storage.
Regional Storage
The regional storage offered by Cloud Storage is ideal when your organization wants to use the data locally. It gives you added throughput and performance by storing your data in the same region as your compute infrastructure. This is a great choice for internal use cases such as data and analytics and machine learning jobs.
For data that will be accessed less often, Cloud Storage offers NearLine or ColdLine Storage.
NearLine Storage
NearLine is best for data you don’t expect to access more than once per month, such as multimedia file storage or online backups.
ColdLine Storage
ColdLine is best for data that you plan to access at most once per year, such as archive data or as a backup for disaster recovery.
Google Cloud Products for Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Machine Learning is a way to use standard algorithms to get predictive insights from data to make repeated decisions. For ML models to be successful, they require large amounts of data.
Google Cloud’s AI platform is a unified, simply managed platform that makes machine learning easy to adopt by mainstream analysts and developers, not just data scientists. It provides modern ML services with the ability to generate your own tailored models or use pre-trained models so that you can add innovative capabilities to your own applications.
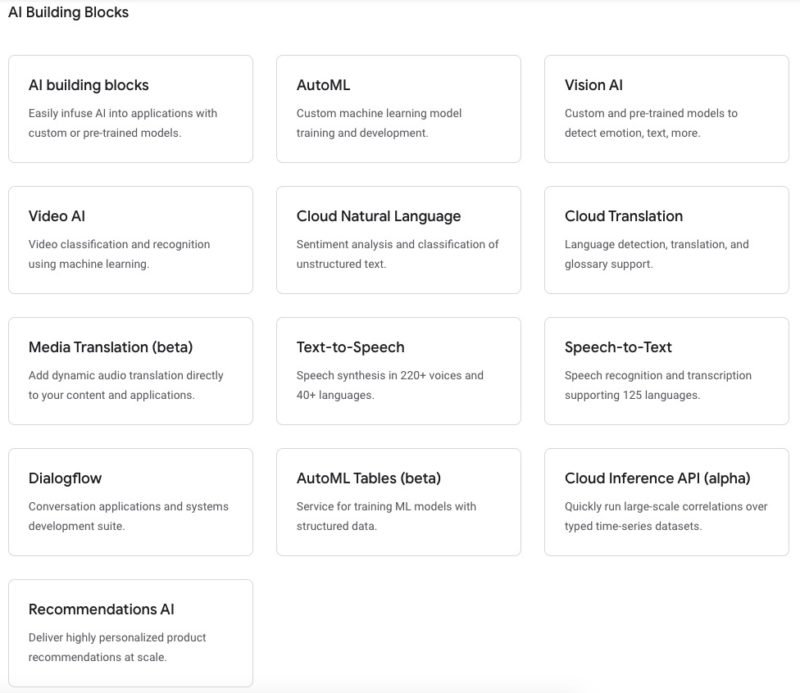
AI Building Blocks
- Video AI
- AutoML
- Cloud Natural Language
- Text-to-Speech and Speech-to-Text
- Vision AI
- Recommendations AI
Source: Google Cloud
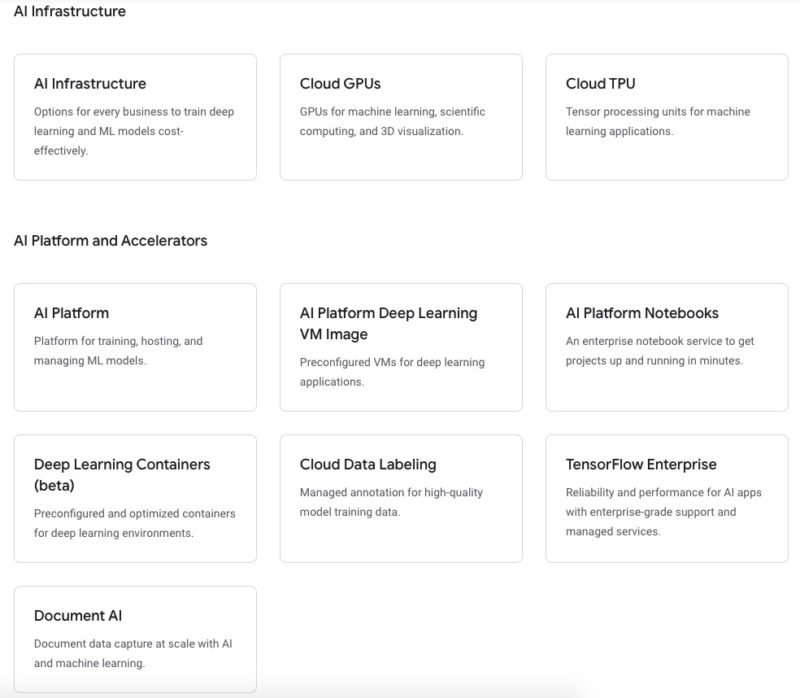
AI Infrastructure, Platform, and Accelerators
- Cloud GPU
- Cloud TPU
- AI Platform
- Cloud Data Labelling
- TensorFlow Enterprise
- Document AI
Source: Google Cloud
It also includes Google Cloud’s AI hub, a hosted repository of plug-and- play AI components.
Solutions For Data Scientists
TensorFlow
If you have data scientists who are already working with ML, they might already be using TensorFlow. This is a software library that was first developed for Google’s internal use but is now open source so that everyone can benefit. You can run TensorFlow wherever you like, but GCP is an ideal place for it, because ML models need lots of on-demand compute resources and lots of training data. TensorFlow can also take advantage of tensor processing units, TPUs, which are hardware devices designed to accelerate ML workloads with TensorFlow by 15 to 30X. GCP makes them available in the Cloud with Compute Engine virtual machines.
Each Cloud TPU offers a large amount of performance, and because you only pay for what you use, there is no upfront capital investment required.
Google AI Hub
The AI Hub is a hosted repository of plug-and-play AI components, including end-to-end AI pipelines and out-of-the-box algorithms. If your data scientists need to start work on a new problem, Google’s AI Hub has notebooks samples that they can use to learn about, train, and deploy the new model they need.
Google Cloud Machine Learning Engine
Google Cloud Machine Learning Engine lets developers and data scientists easily build ML models that work on any type of data of any size. It can take any TensorFlow model and perform large-scale training on a managed cluster.
Solutions for Non-Data Scientists
If you have analysts and developers, but no data scientists, Google Cloud’s platform as a service offerings are useful. We can help app developers build smart apps using APIs. APIs, or application programming interfaces, are simple methods and tools to connect various applications. The developer can simply use AI Hub to find an API that will help.
Vision API
Vision API offers powerful, pre-trained machine learning models. The developer can use it to assign labels to images and quickly classify them into millions of predefined categories. Using Vision API, the developer can easily incorporate a pre-trained model into their project.
AutoML Vision API
Categorizing images is sometimes more complex. In this case, the developer could use AutoML Vision API. This API automates the training of your own custom machine learning models. A developer can simply upload images and train custom image models with the easy-to-use graphical interface. Models can be further optimized and exported to an application in the cloud.
Natural Language API
The powerful pre-trained models of the Natural Language API empowers developers to easily apply natural language understanding (NLU) to their applications with features including sentiment analysis, entity analysis, entity sentiment analysis, content classification, and syntax analysis.
There are many more APIs available on Google Cloud.
Cloud Discover
In innovative applications for machine learning, several applications need to be combined. This is why Google Cloud’s Professional Services offer Cloud Discover. Cloud Discover is a process used to help customers discover ML use cases, evaluate the feasibility of those projects, and choose pilot projects that they can then implement and take to production.
Google Cloud Products for Security and Identity
Security and Identity Management are important aspects of any modern day business. Google Cloud offers a range of products and services in the Security and Identity space.
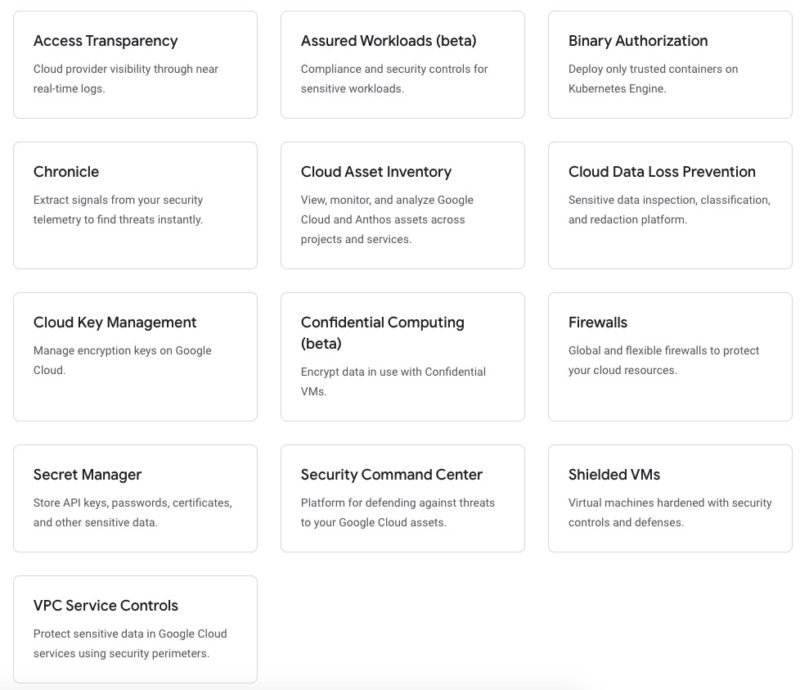
Security and Identity
- Firewalls
- Binary Authorization
- Access Transparency
- Cloud Data Loss Prevention
- Cloud Key Management
- Chronicle
- Shielded VMs
- Confidential Computing (beta)
Source: Google Cloud
Business Transformation with Google Cloud
Improvement vs 10X mindset
Improvements, as the name suggests, are aimed at making something better. For example, if the highways are made better between City A and City B and speed limit increased from 70 miles per hour to 80 miles per hour, it is considered an improvement project. It causes a speed improvement of 14%.
10X mindset enables us to innovate and disrupt the status quo. For a 10x mindset person, a 10 – 15% improvement is not enough. In our example above, the highway speed cannot be increased by a lot more than 15% because of multiple limitations. A 10x person would recommend something like a hyperloop that can transport people at 700 miles an hour
Quick Wins, Disruption, Development and Transformation
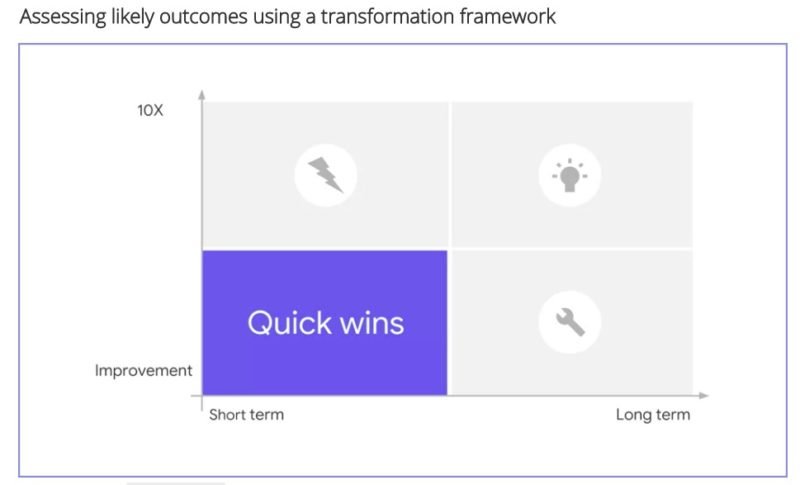
Quick Win – Short Term Improvements
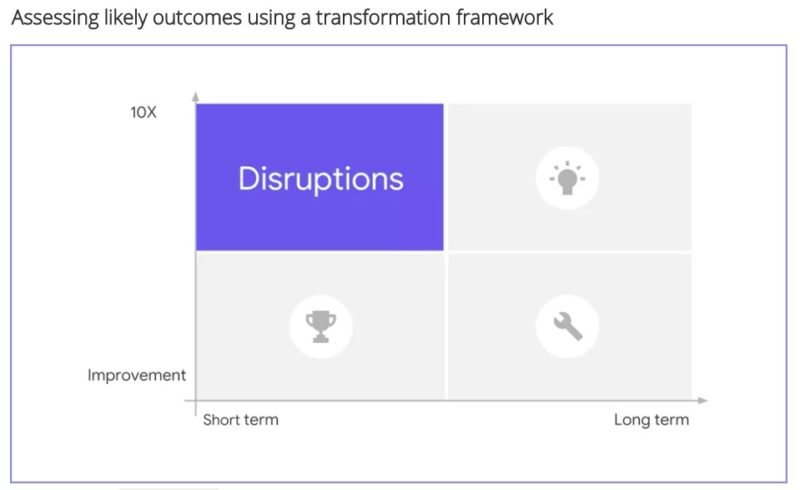
Disruption – 10X Value Creation in Short Term
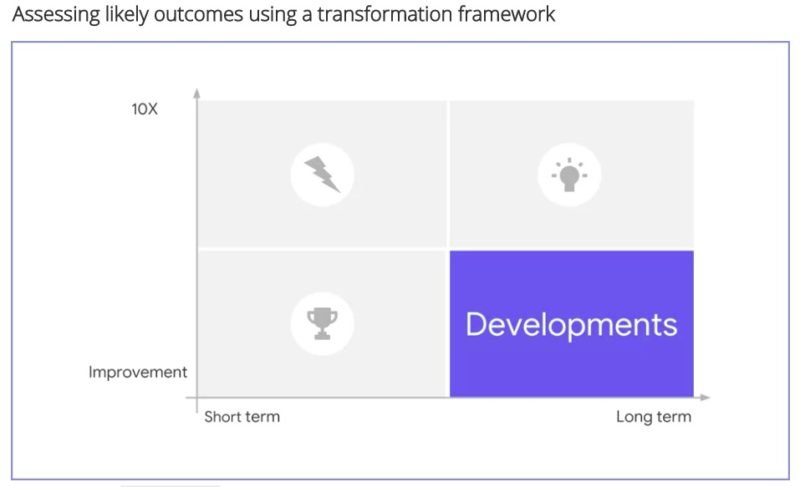
Development – Improvements Carried Out in Long Term
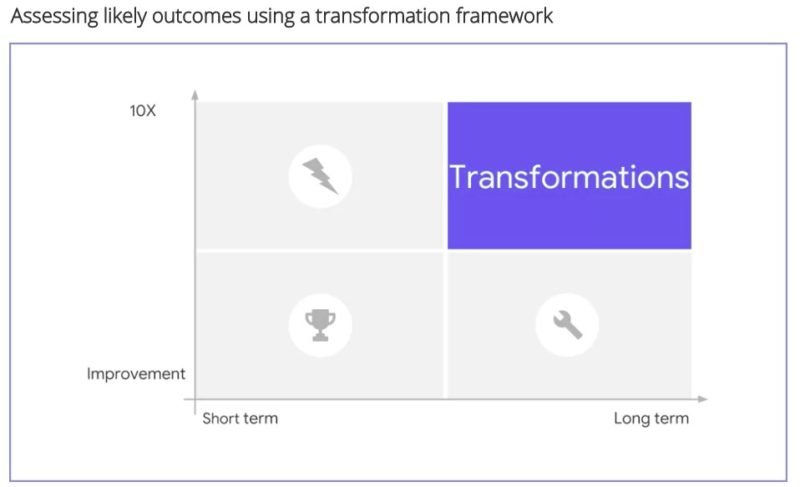
Transformation – Long Term Projects With a Capability to Deliver 10X Impact
How to Identify a True Transformation Project?

If you answer YES to these questions, you are looking at a transformation opportunity.
- Does the challenge require a change in people, process, and technology?
- Will the challenge require a completely new approach?
- Do you need a new strategy to conquer and implement the challenge?
9 Steps in Business Transformation
1. Start with Why: Why does the Business Exist?
Without focusing on ‘how’, get the essence of why the business exists. The transformation must align with the business’ core mission and vision.
2. Ask the Key Question
Aim Straight
Be specific enough in framing the key question. It should not be too vague.
Shoot For The Moon
Look for the 10X value from your transformation opportunity
3. Brainstorm the Solutions (come with 3+)
Without worrying about how crazy the idea sounds or how feasible it is, come up with potential solutions to achieve 10X impact. List out all the potential solutions, with a suggested minim of 3.
- Potentail Solution 1
- Potential Solution 2
- Potential Solution 3
4. Evaluate the Solutions for Best Fit using a Matrix
After brainstorming the solutions, it is time to evaluate them against some criteria. It is good to test them for their feasibility, differentiation, and business impact.
Feasibility
Does the technology exist?
Is the consumer base ready to consume the solution or it needs some socializing?
Differentiation
How different is the solution from status quo?
Can the competitors replicate?
Business Impact
How much benefit can we get out of this idea?
What would it cost us to implement the idea?
5. Define a Roadmap Using Smaller Projects to Reach Your 10X Goal
The smaller goals can be a mix of Quick Wins, Disruptions, and Developments to reach your end goal: Transformation
The ideal roadmap looks like this:
Quick Win -> Disruption -> Development -> Transformation.
6. Build Your Data Strategy
Gather the information in three buckets (User, Corporate, Industry) and categorize them into what you have, what you don’t currently have but can acquire, and what data is neither available nor acquirable.
- Define everything you need to know in order to reach your end goal.
- Categorize these data sets according to what you have, what you need to acquire, and if it doesn’t exist, what you need to then capture or collect.
- for the data sets you need to capture, brainstorm on how you can do it.
User
- What kind of data do you already have?
- What kind of additional data, available elsewhere, do you need?
- If the data doesn’t exist – how can we capture or collect?
Corporate
- What kind of data do you already have?
- What kind of additional data, available elsewhere, do you need?
- If the data doesn’t exist – how can we capture or collect?
Industry
- What kind of data do you already have?
- What kind of additional data, available elsewhere, do you need?
- If the data doesn’t exist – how can we capture or collect?
7. Capture the Critical Data That Cannot be Acquired
- Can placing some sensors help you capture data?
- How can you incentivize the customer to reveal their preferences? Is it a good idea?
- Can observing the customer behavior be a good data source?
New data captured will require upfront costs, and cost of storing securely. What are the other use cases where this data can be leveraged? This will help build a robust business case for capturing the new data.
8. Build a Compelling Business Case
Description
- What is the business problem or opportunity?
- Who is the Customer? Who is the end user?
- How is the problem being addressed now?
Outcomes
- Business
- Strategic
- Technical
Success Metrics – Financial and Non-Financial
- Costs
- Benefits
- Return on Investment
- Other Metrics
- Expected Adoption Curve
Constraints + Risks and Mitigation Plans
- Regulatory Risks
- Technical Hurdles
Play Devil’s advocate and get your colleagues to poke holes in the project plan.
- Why might the project fail?
- What can be the good, bad, ugly outcomes?
- Identify and propose mitigation for all these steps.
Target Environment
9. Socialize The Business Case
Create a small presentation with the following sections to communicate and get buy-in from decision-makers. This is different from a detailed business case report that you will build.
Concise and Memorable Title
It could be an acronym or a short 2-3 word project title
Catchy Sentence or Caption (Optional)
A caption can quickly introduce the idea of the project
Pitch: Communicate the value directly, in succinct and clear language
A pitch expands on the idea and the value it can bring to the business. A clearly delivered message stating the value in a succinct manner will help grab the attention of the decision-makers.
Business Impact
Expand on the value delivered in the business impact section. Show how the idea is aligned with the business’ long-term goals and how you will know when the project is successful. Make sure to address the following questions:
- How does the project meet organization objectives?
- How will the success of your project be measured?
- Will the project create new value for the business? How much?
The post contains a reference to the Google Cloud website and training videos on Coursera



